What is Neurology?
People who are having problems with their senses, such as touch, vision, or smell, may also need to see a neurologist. Problems with senses are sometimes caused by nervous system disorders.
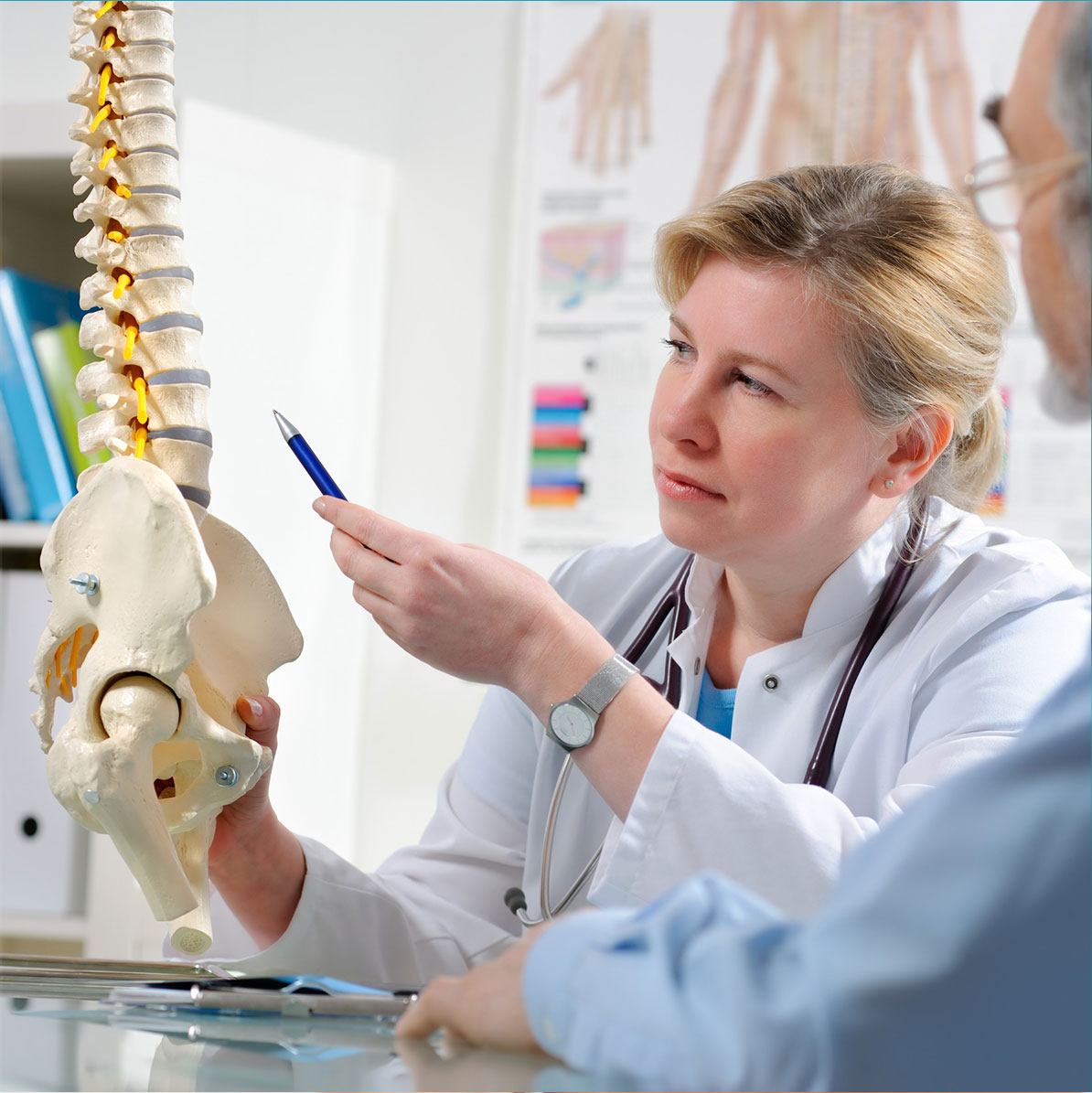
Neurologist
ADHD
A chronic condition including attention difficulty, hyperactivity, and impulsiveness.
Huntington’s Disease (HD)
An inherited condition in which nerve cells in the brain break down over time.
Migraines
A headache of varying intensity, often accompanied by nausea and sensitivity to light and sound.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
A nervous system disease that weakens muscles and impacts physical function.
Alzheimer’s
A progressive disease that destroys memory and other important mental functions.
Brain Tumor
A cancerous or noncancerous mass or growth of abnormal cells in the brain.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
A disease in which the immune system eats away at the protective covering of nerves.
Back Pain
A common, painful condition affecting the lower portion of the spine.
Sleep disorders
Changes in sleeping patterns or habits that can negatively affect health.
Bell’s Palsy
Sudden weakness in the muscles on one half of the face.
Myasthenia Gravis
A weakness and rapid fatigue of muscles under voluntary control.
Seizures
Seizures are symptoms of a brain problem caused by sudden, abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
A numbness and tingling in the hand and arm caused by a pinched nerve in the wrist.
Peripheral Neuropathy
Weakness, numbness, and pain from nerve damage, usually in the hands and feet.
Guillain-Barre Syndrome
A condition in which the immune system attacks the nerves.
Parkinson’s Disease
A disorder of the central nervous system that affects movement, often including tremors.
Myopathies
Muscular disease where primary symptom is muscle weakness due to dysfunction of muscle fiber
Stroke
Damage to the brain from interruption of its blood supply.
Dementias
A group of thinking and social symptoms that interferes with daily functioning.
Stroke
Vivamus libero ligula, tincidunt vel venenatis eu, vehicula venenatis purus. Duis at lorem venenatis, mattis nunc sollicitudin.
Chronic pain
Persistent pain that lasts weeks to years.

